
-
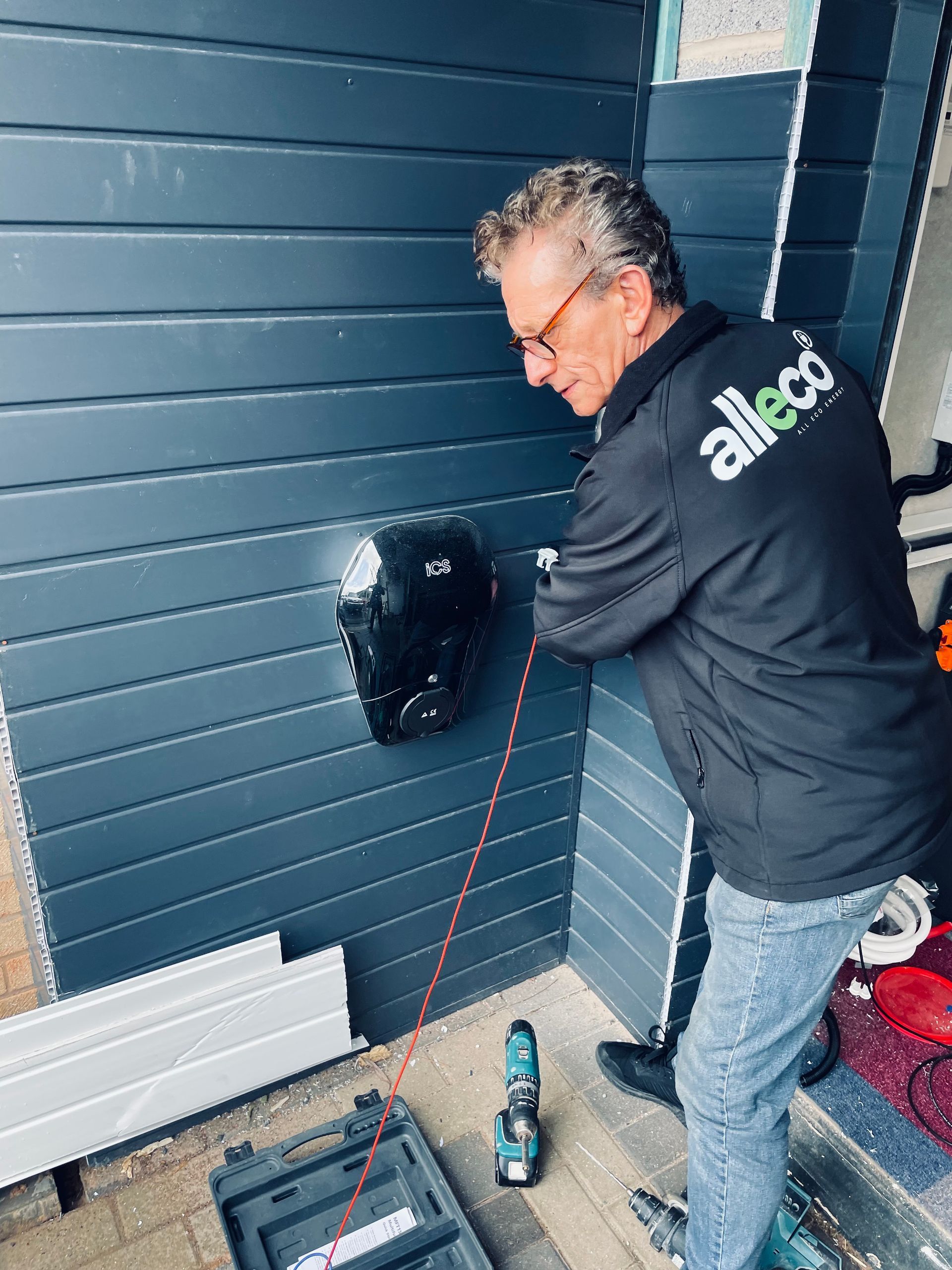
All of our technicians are trained and certified
-
Satisfaction guaranteed on every project
-
Three generations and 20+ years experience
-
Residential and commercial services

-
All of the UK to go fully Electric by January 2030 Net Zero emisions
The Government has confirmed that the ban on new petrol and diesel cars has been moved forward to 2030, following a lengthy consultation. There are some exceptions to the ban, with some plug-in hybrids (PHEVs) and some full hybrids still able to be sold up until 2035.
Transport is the UK’s largest emitting sector, accounting for more than 30% of national carbon emissions. While this does include aviation, road vehicles account for around 19% of all UK emissions. With the ban confirmed, the Government has wasted little time in incentivising the market to promote EV innovations.
The Government’s new £20m fun will assist research and development competition, for EV technology innovations. Funding could potentially support zero-emissions emergency vehicles, charging infrastructure and battery recycling.
It builds upon the £1.3bn EV charging infrastructure commitment unveiled last year. Reports suggest that the UK needs to install five times as many EV charging points to meet its net-zero target.

-
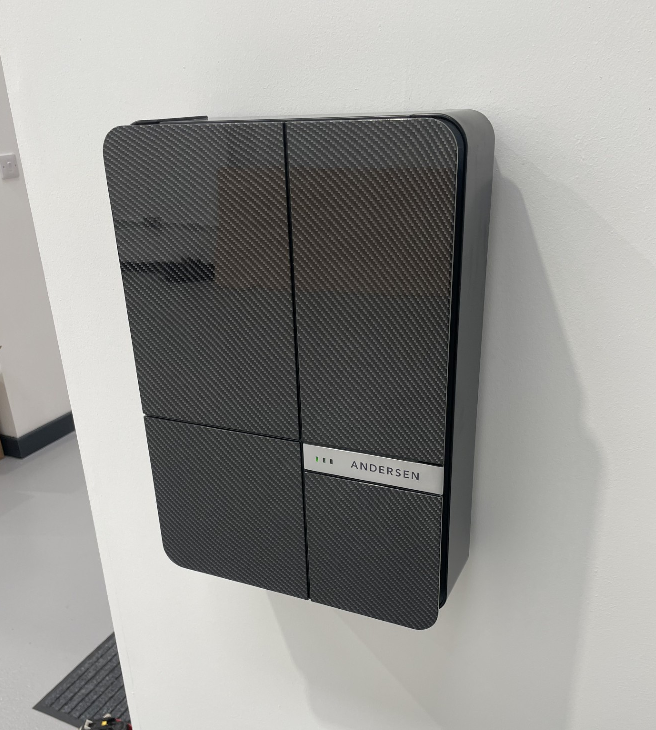
EV & Solar
Standard Installation + Integrated Control to Maximize use of your Existing Solar PV and Battery storage system.
-
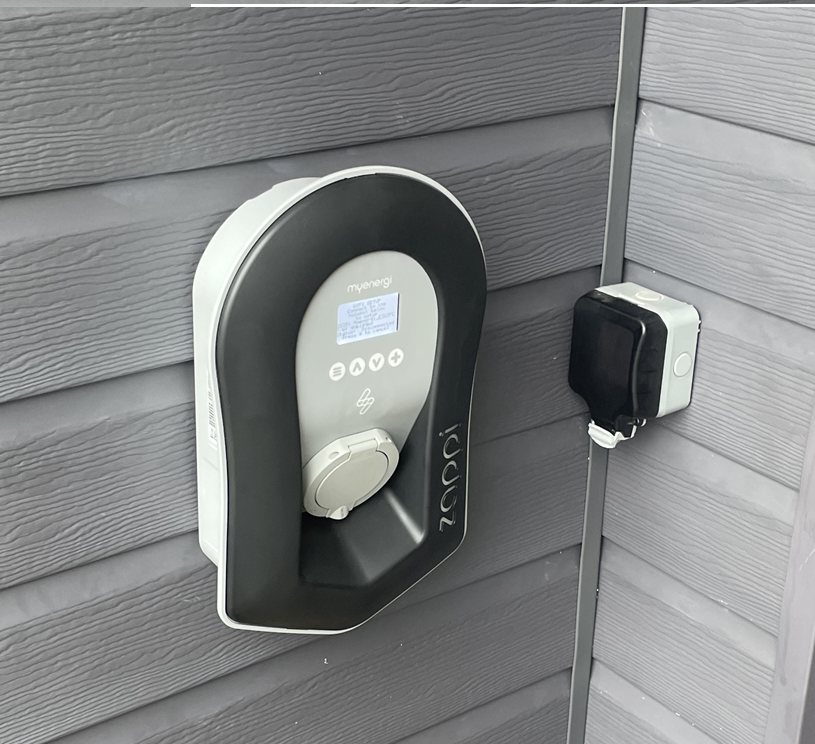
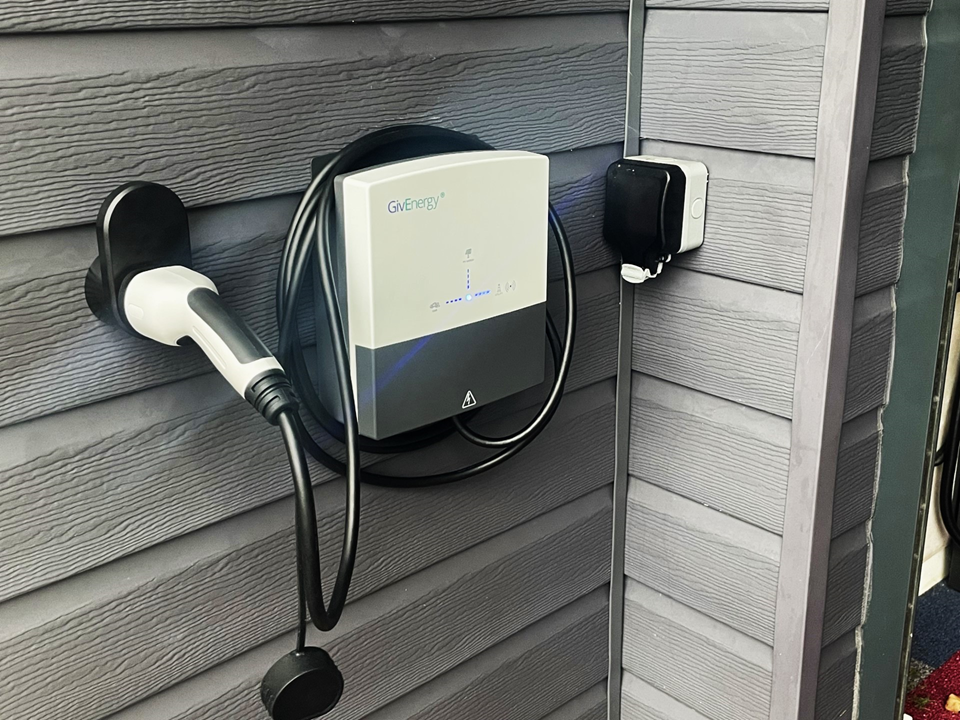
Wall Mounted EV
Standard Installation + Integrated Control to Maximize use of your Existing Solar PV SYSTEM £400.00 -£650.00
Tesla Powershare Gateway
Use your Tesla Car battery to power your home with Powershare

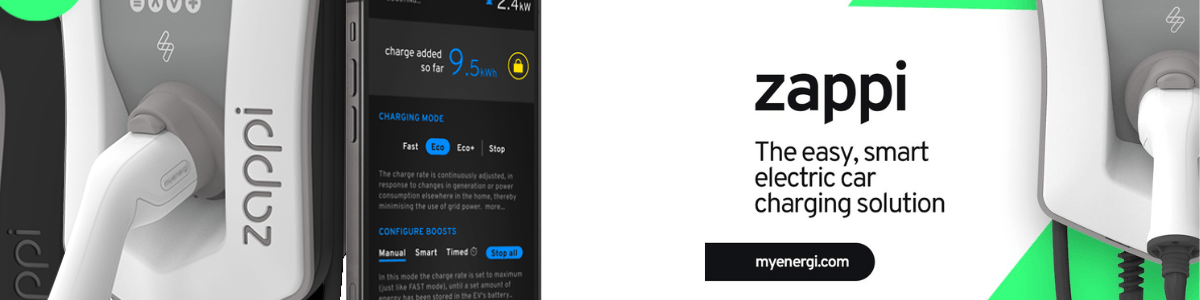


How do Charge Points Work & How to Calculate Charging Times
Mode 1 & 2 slow charge can be achieved over about 7 or 8 hours and works by attaching your car battery to a general electricity supply. Slow chargers typically operate at 3 kW (13-16 Amps) and you can use a normal plug socket but it is advised to have a dedicated unit installed at home or work. The first initial public charge points were of this type but they are now being replaced by faster units.
Mode 3 Fast chargers deliver between 7 and 22 kW and provide a much quicker load time of three to four hours. As of September this year there were over five and a half thousand fast chargers in the UK.
Mode 4 Rapid chargers can come in either AC or DC. AC chargers up to about 43 kW can provide an 80% charge in about 30 minutes. A DC charger provides up to 50 kW and delivers a similar result. Whether your EV can take either the higher AC or DC charging will depend on your model of car and the kind of attachment you have.
Ultra-rapid charger delivers either 100kW, 150kW or 350kW. The most common rapid charger in the UK is the 50kW device.
Connectors also vary depending on the amount of charge you can have and whether it is AC or DC. You may need to buy different cables including a portable charging cable that allows you to safely perform a charge at home.
Remember this Principle
(charging calculation)
Example: Lets assume you arrive home at the end of the day in your kia e-Niro and are at 50% charge, and your battery size is (64kWh). You have a 7.4KW Home charger and you want to go from 50% (32 kWh) to 100% (64kWh), thats 32 kWh shortfall to make up.
All you need to calculate is the time its takes your "specific charger" to charge your "specific battery size", and the following calculation is:
- 32 kWh ÷ 7.4kWh = 4.32 hours ( It takes 4.3 hours to charge your 50% battery to full charge). From 0% to 100% it would take 64kWh ÷ 7.4kWh = 8.64 hours.

We will get back to you as soon as possible.
Please try again later.




Company
- Alleco Energy Installers Ltd
- Registered Company: 14338339
- Website: www.alleco-energy.co.uk
- Email: office@alleco-energy.co.uk
- Support: James@alleco-energy.co.uk
All Rights Reserved | alleco energy Installers LTD
Photovoltaic & Wind Disclaimer:
Under no circumstances should the daily or annual performance examples in our photovoltaic Research Hub be assumed an absolute indicator of solar panel performance with regards to your own property, and we cannot be held responsible for any decisions made by anybody based on the information provided within our articles.
All Rights Reserved | alleco energy Installers LTD
















